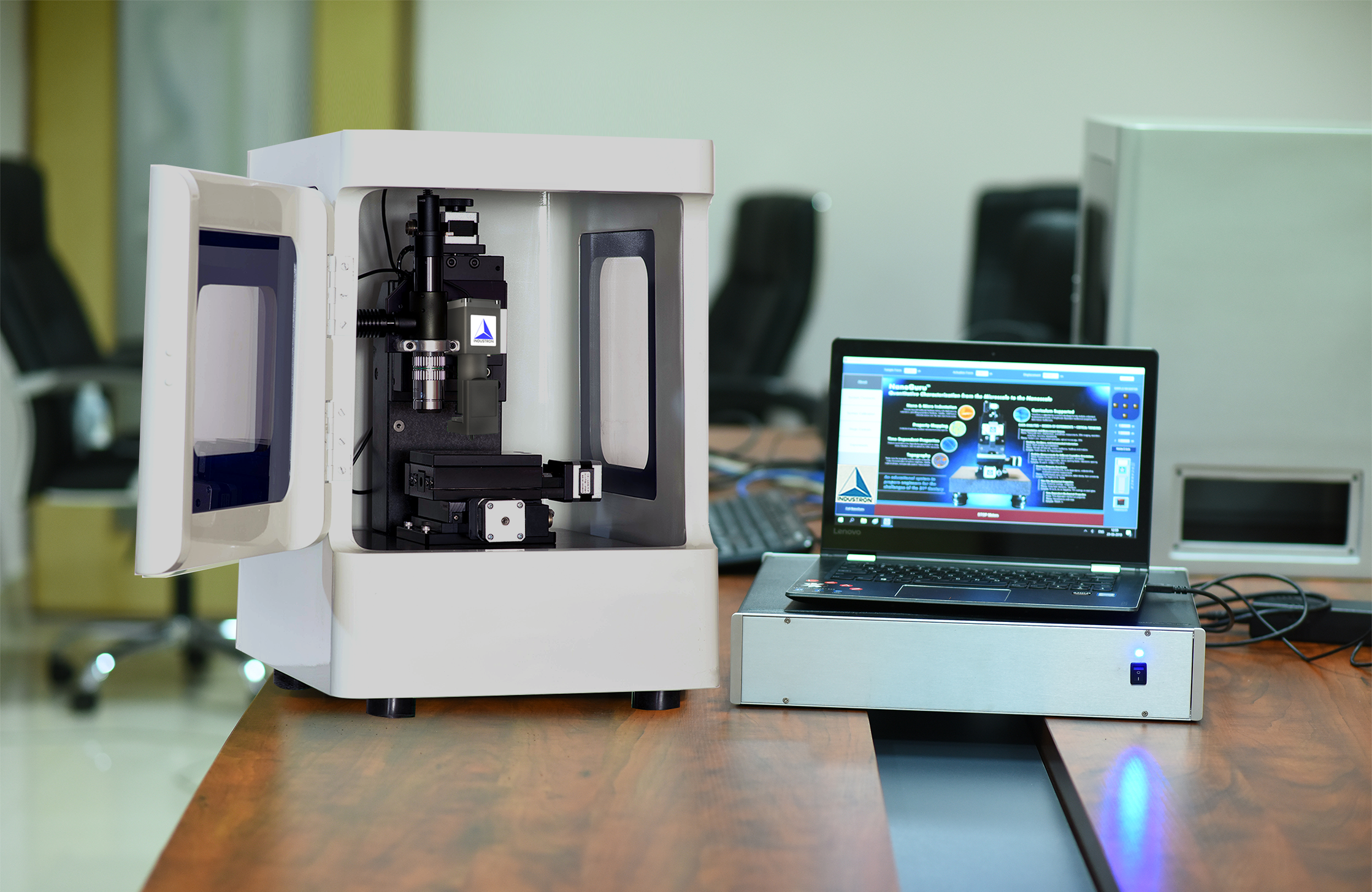
A High Throughput Nanomechanical Test Instrument
Features
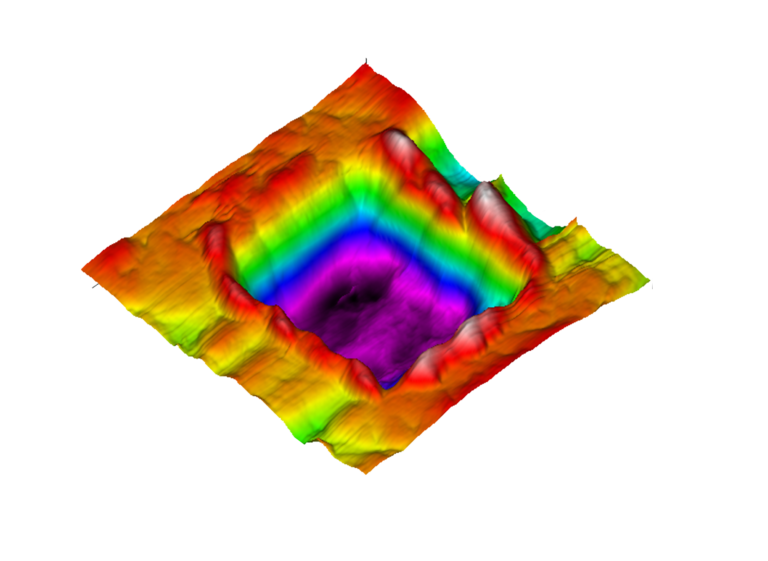
Scanning nanoWear
Helps to quantify wear volumes and wear rate at sub micron level along with in-situ SPM imaging capability. Multiple pass wear tests can be performed at different normal scanning force on the surface of the material being tested.
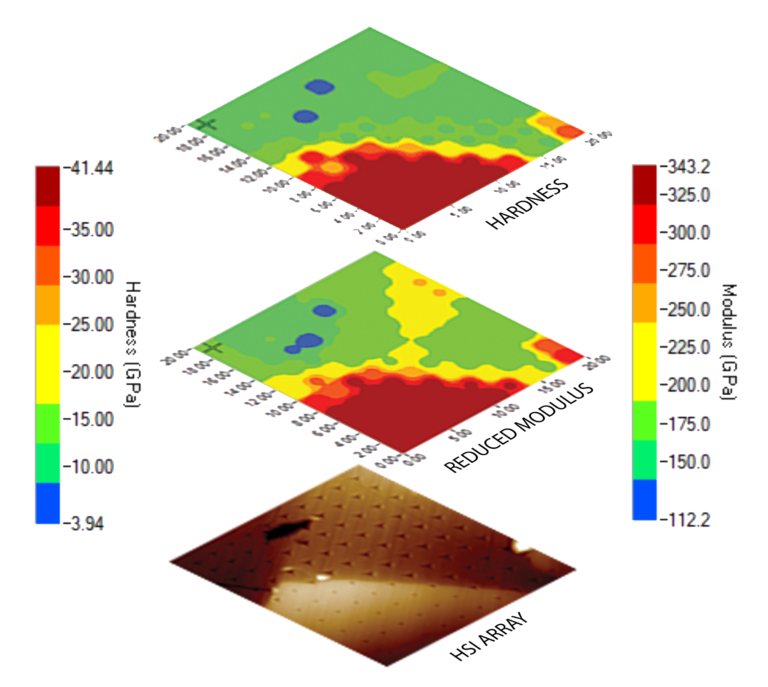
High Speed Indentation
High speed indentation is 300X faster than conventional indentation. It allows to perform microstructural mapping and to obtain statistical distribution of mechanical properties in quick time.
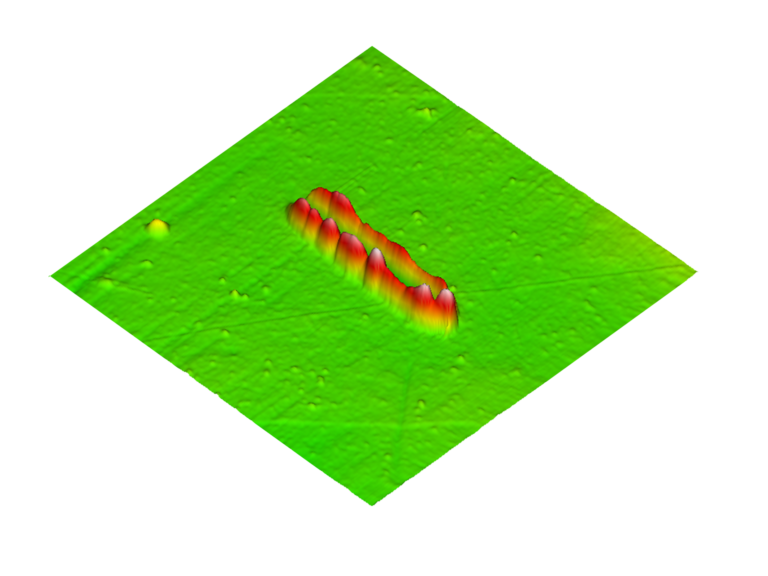
nanoScratch
A versatile tool for the tribological characterization of both thin film and bulk material. It gives the quantitative measure of force and displacement data in lateral and normal directions for calculating the bulk material coefficient of friction and critical load of thin film delamination.
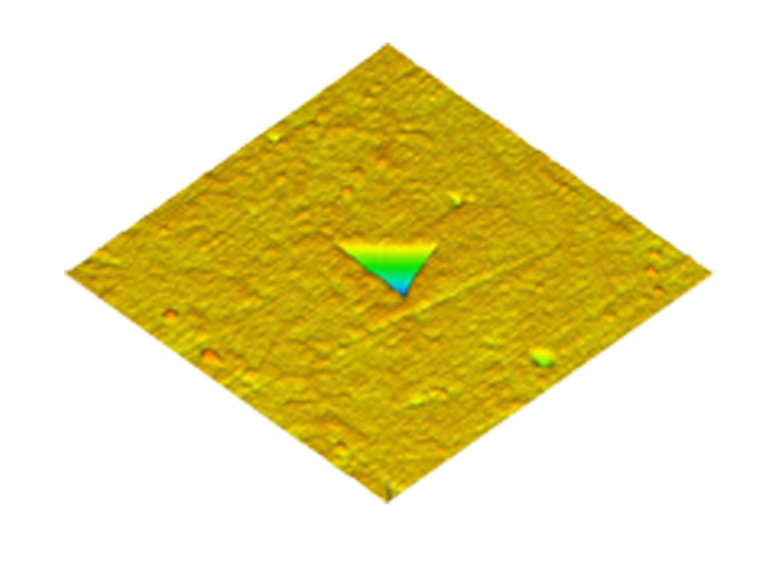
Quasistatic Nanoindentation
Nanoindentation is an instrumented mechanical property measurement technique to measure properties such as Hardness and Modulus at nanometer length scale. Nanoindentation gives localized mechanical properties quantitatively by applying a force to drive the indenter probe into a sample surface and measuring the depth of indent during loading and unloading. Test can be performed in either load-controlled or displacement-controlled feedback mode.
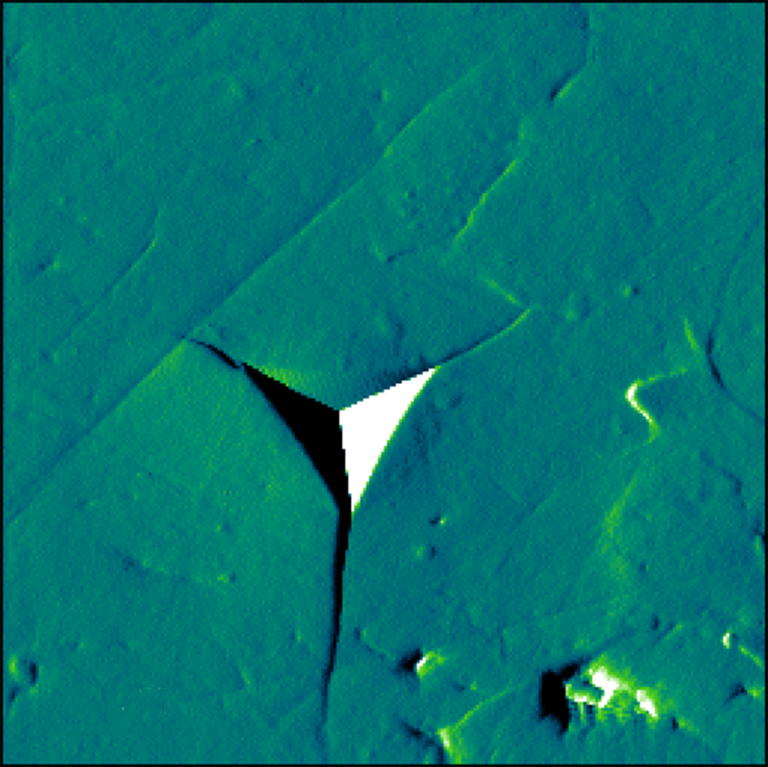

Fracture Toughness
Fracture toughness of brittle bulk materials is an important measure of the resistance of these materials to crack propagation and fracture. It was commonly evaluated using a conventional microindenter however, the inherent bluntness of the microindenter tip required large forces to produce the cracks necessary for the analysis. Measuring hardness and modulus of thin films using microindentation requires tedious work to correct for substrate effects, which makes the fracture toughness of thin films difficult to determine. Nanoindentation offers a number of advantages for the measurement of the fracture toughness of thin films and very small volumes.
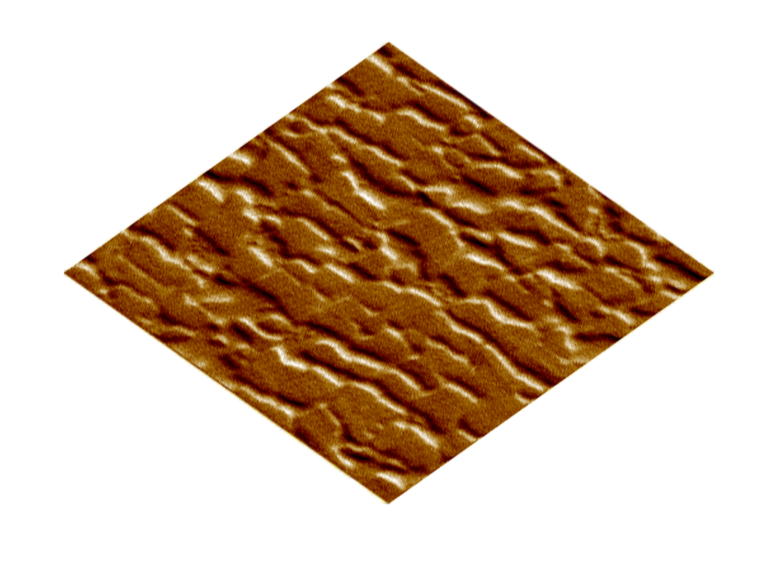

In-situ SPM Imaging
Unique feature which gives a nanometer resolution 3D topographical image of the sample surface by raster scanning the surface with the indenting probe. In-situ SPM functionality enables researchers to select and perform site specific indentation experiments with an accucracy of +/- 10 nm.